- Memory = a brain function.
- See also: Dementia
- See also: Alzheimer
- See also: Testing for Dementia/Alzheimer
- Causes | Treatment | Cures | Testing | Preventing | Care | Resources
-
-
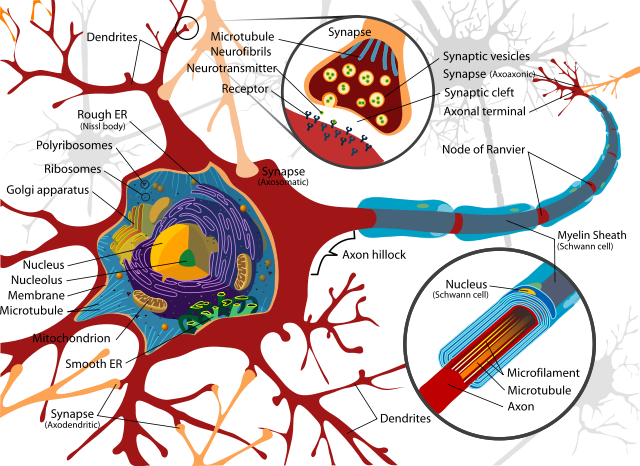
- Dementia is an umbrella term for a group of symptoms contributing to a decline in memory, thinking, reasoning and social abilities. It’s progressive.
- 7 Sneaky Signs You Could Have Cognitive Decline
- LMTX = Methylene blue
- TauRx Therapeutics - Wikipedia - LMTX is an altered version of Methelene blue.
- Methylene blue - Wikipedia
- LMTX is not effective if combined with other Alzheimer drugs.
- Edutopia
- 1440
- Everything Zoomer
- See also: Testing for Dementia/Alzheimer
- Early Indicators of Dementia: 5 Behaviour Changes to Look for After Age 50 - Everything Zoomer
- What You Should Do - And Not Do - to Reduce Your Risk of Dementia - Everything Zoomer
- Report Suggests Alzheimer’s Research May Have Been Fabricated; What Does This Mean for Diagnosis and Treatment? - Everything Zoomer
- Exercise
- Treat high blood pressure
- Stop smoking
- Treat hearing loss
- Floss your teeth regularly
- Convince your government to fund research
- Zika Virus May Cause Alzheimer-like Symptoms in Adults - Everything Zoomer
- ExtremeTech
- The Globe and Mail
- Data show just how much exercise can lower Alzheimer’s risk - The Globe and Mail
- A gene variant known as APOE-e4 is thought to play a role in up to one-quarter of Alzheimer’s cases.
- If you want to improve your odds, you should exercise no matter what your genes say.
- A need for change in the unbalanced approach to Alzheimer’s - The Globe and Mail
- 72 per cent of Alzheimer patients are female.
- Age is the biggest risk factor for dementia.
- Women are 2.5 times more likely to suffer from depression than men.
- Only 5 per cent of people with Alzheimer’s are genetically predisposed to have the disease.
- Anxiety may accelerate slide into Alzheimer’s - The Globe and Mail
- Anxiety may accelerate the decline into Alzheimer’s disease in older patients with mild memory problems.
- People with anxiety disorders have higher levels of the stress hormone cortisol, which has been shown to damage the hippocampus, a brain structure important for memory processing and emotion.
- Follow the MIND diet to stave off Alzheimer’s - The Globe and Mail
- Mediterranean diet
- DASH =Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension
- MIND diet =Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay
- Antipsychotics shouldn’t be a default drug for dementia - The Globe and Mail
- Researchers link common over-the-counter drugs to dementia - The Globe and Mail
- GreenMedInfo.com
- Health.com
- HealthAfter50.com | UC Berkley School of Public Health | Health and Welness Alerts
- HealthLine.com
- 10 Early Symptoms of Dementia: Be Aware of Subtle Signs - Thanks to Mitchell Abbott for recommending this site.
- Neurology | Midlife cardiovascular fitness and dementia | Neurology
- Neurotrack
- Neurotrack, the winning health startup at SXSW — Tech News and Analysis - 2013-03-13 - Neurotrack, a startup built on years of neuroscience research, says it can identify patients at risk for developing Alzheimer’s years before the onset of the condition.
- Neurotrack - Transforming the diagnosis & treatment of Alzheimer’s
- New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM)
- Glucose Levels and Risk of Dementia — NEJM - 2013-08-13
- Higher glucose levels may be a risk factor for dementia, even among persons without diabetes. (NIH)
- Glucose Levels and Risk of Dementia — NEJM - 2013-08-13
- New York Post
- New York Times -|$$$|- (CDN$20/4weeks)
- Nurse
- Behavioral Challenges: A Nurse's Practical Tips for Understanding Alzheimer's | NursingEducation - Thanks to Sarah Breckon @nursingeducation.org for recommending this site.
- An overview of the stages of Alzheimer’s disease
- How to recognize common behavioral challenges in Alzheimer’s patients
- Tactics to help manage behavioral challenges such as aggression, anxiety, depression, confusion, sundowning, or wandering
- Medical and non-medical intervention options available to Alzheimer’s patients and their caregivers
- Additional resources recommended by our nursing staff
- Behavioral Challenges: A Nurse's Practical Tips for Understanding Alzheimer's | NursingEducation - Thanks to Sarah Breckon @nursingeducation.org for recommending this site.
- MentalFloss
- Reader's Digest = rd.ca
- Dementia Breakthroughs Offer New Hope | Reader's Digest Canada
- Alzheimer’s as an autoimmune disease of the brain. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia, accounting for up to 80 percent of all diagnoses.
- Types
- beta-amyloid proteins
- tau proteins
- Lewy body dementia | Alzheimer Society of Canada - alpha-synuclein protein
- vascular dementia - Strokes, transient ischemic attacks, blood-vessel disease
- frontotemporal dementia
- Mixed dementia
- Treatments
- Cholinesterase inhibitors - does not limit the disease’s progress
- memantine - does not limit the disease’s progress
- Aducanumab - has not been proven to slow cognitive decline
- lecanemab (Leqembi) - unproven - rate of memory and cognition decline was 27 percent less - serious side effects
- donanemab - slows the rate of cognitive decline from Alzheimer’s by about one third. - serious side effects
- Stem cell therapy
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation
- Risk Factors
- Hearing loss (leading to isolation)
- Time socializing
- Lack of daily exercise
- Smoking and other air pollution
- Traumatic brain injury
- Heavy drinking
- High blood pressurs
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- 13 Early Signs of Dementia (and How to Spot Them) | Reader's Digest
- Obvious Signs of Dementia I Missed in My Own Mother | Reader's Digest
- 15 Alzheimer's Research Breakthroughs That Give Hope for the Future
- Dementia Breakthroughs Offer New Hope | Reader's Digest Canada
- Self
- Telegraph
- WSJ = Wall Street Journal
-
- Addiction ...
- Alzheimer & Dementia
- see also: Dementia
- see also: Memory
- Alzheimer’s disease is just one of 70 causes of dementia (an umbrella term for memory loss due to changes in the brain).
Not everyone who has dementia has Alzheimer’s – it can also be part of Parkinson’s disease or the result of a stroke, for example. - Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a condition that, in many cases, is a precursor to Alzheimer's disease.
- Alzheimer Disease (la maladie d'Alzheimer) accounts for 64% of all Dementia cases.
- We all have a 50 percent chance of developing Alzheimer's disease after age 85. Alzheimer's disease is not a normal part of aging.
- Alzheimer's Could Be Linked to a Common Virus You Already Have : ScienceAlert
- What Is Alzheimer's Disease And Is There a Way to Treat It? : ScienceAlert
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 in brain and risk of Alzheimer's disease - The Lancet
- The common cold sore virus, which is often caught in childhood, usually stays in the body for life – quietly dormant in the nerves. Now and then, things like stress, illness or injury can trigger it, bringing on a cold sore in some people.
- herpes simplex virus type 1
- People who have a certain version of a gene (called APOE-e4) that increases their risk of Alzheimer's, and who have been infected with this virus, have a risk that is many times greater.
- Antiviral treatment associated with reduced risk of clinical Alzheimer's disease-A nested case-control study - PubMed
- Those who had the shingles vaccine were less likely to develop dementia at all.
- Alzheimer's May Not Actually Be a Brain Disease, Expert Reveals : ScienceAlert
- Scientists identify a significant connection between vaccinations and Alzheimer's Disease
- Alzheimer’s might not be primarily a brain disease. A new theory suggests it’s an autoimmune condition.
- In July 2022, Science magazine reported that a key 2006 research paper, published in the prestigious journal Nature, which identified a subtype of brain protein called beta-amyloid as the cause of Alzheimer’s, may have been based on fabricated data.
- Dementia= a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases.
- Alzheimer Disease = AD is the most common form of dementia. AD is a progressive, degenerative brain disease. AD affects memory, thinking, and behaviour.
- Vascular dementia
- Frontotemporal dementia
- Semantic dementia
- Lewy bodies dementia.
- etc... (It is possible for a patient to exhibit two or more dementing processes at the same time, as none of the known types of dementia protects against the others.)
- Dementia - Wikipedia - la Démence
- Dementia is a serious loss of global cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging. It may be static, the result of a unique global brain injury, or progressive, resulting in long-term decline due to damage or disease in the body. Although dementia is far more common in the geriatric population, it can occur before the age of 65, in which case it is termed "early onset dementia". Dementia is not a single disease, but rather a non-specific illness syndrome (i.e., set of signs and symptoms) in which affected areas of cognition may be memory, attention, language, and problem solving. It is normally required to be present for at least 6 months to be diagnosed; cognitive dysfunction that has been seen only over shorter times, in particular less than weeks, must be termed delirium. In all types of general cognitive dysfunction, higher mental functions are affected first in the process.
- Symptoms of dementia can be classified as either reversible or irreversible, depending upon the etiology of the disease. Less than 10% of cases of dementia are due to causes that may presently be reversed with treatment.
- Alzheimer's disease - Wikipedia
- Alzheimer Society of Canada - Société Alzheimer du Canada
- Alzheimer’s Association (US)
- Alzheimer’s Society (UK)
- Legal & Financial
- Legal and Financial Planning for Alzheimers | RequestLegalHelp.com - Thanks to Destinie Wallis for recommending this site.
- Alzheimer's & Dementia Legal & Financial Resources | Fiscal Tiger - Thanks to Heidi Paris for recommending this site.
- ************
- Alzheimer's transmitted from person to person
- Iatrogenic Alzheimer’s disease in recipients of cadaveric pituitary-derived growth hormone | Nature Medicine
- The people described in the study had all been treated as children with a type of human growth hormone taken from dead donors (cadaver-derived human growth hormone or c-hGH). There is no suggestion the protein, amyloid-beta, can be passed on in day-to-day life or during routine medical or social care.
- After 1985, c-hGH was replaced with a synthetic growth hormone that did not carry the risk of transmitting CJD (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease).
- Anticholinergics - Medications for over-active bladders could increase (by 22%-33%) the risk of developing dementia. The pills, called anticholinergics, work by reducing the activity of certain muscles to stop the bladder contracting. Those prescribed oxybutynin hydrochloride had a 31 per cent higher risk of dementia, and those on tolterodine tartrate had a 27 per cent increased risk. Some types of anticholinergics weren't linked to an increased chance of dementia. These were darifenacin, fesoterodine fumarate, flavoxate hydrochloride, propiverine hydrochloride, and trospium chloride. With the non-anticholinergic drug called mirabegron, data weren't clear. Previous studies have highlighted oxybutynin, sold under the brands Aspire, Ditropan, Kentera, can be a particular risk as it has a smaller molecule size than other types.
- Causes of Dementia
- Diet - Sugar - Carbohydrates
- mould
- vasculatory/circulatory problems
- chronic hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Aggressively lowering elevated blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and perhaps Alzheimer's disease.
- depression
- Depression may be an early symptom of Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
People who are depressed have an increased risk for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease—that is, blockages in the arteries that impede blood flow to the heart and brain.
Although depression was associated with an 85 percent increased risk for dementia from all causes, the risk for vascular dementia was 250 percent.
- Depression may be an early symptom of Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
- vitamin deficiency
- bacteria & Oral hygiene
- Maintaining healthy gums and teeth is important in reducing P gingivalis. Porphyromonas gingivalis causes corroding of the gums and decaying of the teeth. It is a well-known risk factor for heart and artery disease.
- Plaques give every sign of being the brain's protective reaction against inflammation. They're an effect, not a cause, of the illness that's eating up brain cells – the causes most likely being poor sleep (which prevents elimination of brain waste), toxins, chronic infections, allergies and all the other multiple causes of inflammation. In mice, the oral infection was found to penetrate the brain and increase production of amyloid beta, the Alzheimer's-linked protein. Most laypeople just think of it as brain plaque. P gingivalis also produces poisonous enzymes called gingipains which have previously been linked with two other Alzheimer's-associated proteins called tau and ubiquitin.
- How gum disease could lead to Alzheimer's
- Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer's disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors
- The Cause of Alzheimer's Could Be Coming From Inside Your Mouth : ScienceAlert
- virus
- Herpes - Almost all of us have latent herpes viruses residing dormant within us. The problem comes when they're woken up in the brain by infection, inflammation, a stressful event or a weakened immune system.
- New Evidence Implicates Herpes as a Cause of Alzheimer's – Awakening From Alzheimers
- herpes simplex (HSV1) — the virus responsible for cold sores
- herpes zoster ophthalmicus (shingles affecting the eyes)
- HSV1 sufferers who were treated aggressively with antiviral medication saw the incidence of dementia reduced — by more than ten-fold
- How 2 common viruses may trigger Alzheimer's
- Varicella zoster virus (VZV) is the virus that causes varicella - or chickenpox - in childhood and can cause zoster - shingles - later in life.
- When VZV becomes activated as shingles, it reactivates dormant herpes simplex virus type 1Trusted Source (HSV-1). In 2021, Dr. Itzhaki published a study compiling a significant body of researchTrusted Source showing an association between activated HSV-1 and AD.
- A range of factors has been reported to reactivate HSV-1 from the latent state, including stresses and disease states. Stress, immunosuppression, UV light, and menstruation are possible triggers.
- The authors of the study noted that there is evidence that both HSV-1 and VZV can become activated after COVID-19.
- Cold Sores and Shingles May Be Linked to Alzheimer’s, New Research Indicates | Barron's
- Herpes - Almost all of us have latent herpes viruses residing dormant within us. The problem comes when they're woken up in the brain by infection, inflammation, a stressful event or a weakened immune system.
- genetics?
- Copper (Cu)
- See also: vitamins.htm#traceminerals
- Tap Water May Increase Your Risk of Alzheimer's – Awakening From Alzheimers
- Inorganic copper in drinking water (delivered by copper pipes in the home). Inorganic copper in your bloodstream is called "free copper." And it's NOT good.
- Have your water tested for copper.
- Switch to filtered water.
- The study participants who consumed higher amounts of inorganic copper and who also ate higher amounts of saturated and trans fats suffered a much faster cognitive decline. And the more copper they consumed, the faster their brain functioning went downhill. - Dietary Copper and High Saturated and trans Fat Intakes Associated With Cognitive Decline | Neurology | JAMA Neurology | JAMA Network
- "Organic" copper is the kind you get from the food you eat; it's bound to other elements like carbon and hydrogen. This copper is necessary for the body.
- Copper in multi-vitamins?? Don't take a multivitamin that contains copper. Typical multi-vitamin has 2mg Cu (Copper Sulphate), which is 100% of the daily recommended Cu dose (according to the label).
- The current recommended dietary allowance for copper intake for adults is 0.9 mg/d. However, the study did not find that high copper intake alone was related to cognitive decline. High copper intake was associated with a significantly faster rate of cognitive decline but only among persons who also consumed a diet that was high in saturated and trans fats.
- Hearing loss
- The greater the hearing loss, the greater the chances of developing dementia. Perhaps isolation from other people and resultant lack of physical activity could be involved.
- Isolation, stigma and the resultant lack of physical activity that are linked to hearing and vision problems might have something to do with it.
- Hearing impairment and cognitive decline in senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type. - PubMed - NCBI
- Relationship of hearing impairment to dementia and cognitive dysfunction in older adults. - PubMed - NCBI
- Hearing loss and incident dementia. - PubMed - NCBI
- Hearing impairment and risk of Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. - PubMed - NCBI
- Longitudinal Relationship Between Hearing Aid Use and Cognitive Function in Older Americans. - PubMed - NCBI
- Hearing and visual aids linked to slower age-related memory loss
- Iron ...
- Vision loss
- Sight loss and vision impairment strike more than the eyes alone. They're also linked with cognitive decline and dementia.
- Cataracts - those who accepted surgery had half the rate of cognitive decline compared to those who did not undergo cataract surgery.
- David Perlmutter M.D. - Alzheimer's and Dementia - David Perlmutter M.D.
- A Maverick Scientist has Made an Important New Alzheimer's Discovery – Awakening From Alzheimers
- Guamanian amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism dementia complex (ALS/PDC) = a hybrid form of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS – also known as Lou Gehrig's disease). Boiled bats contained a high dose of a toxin named BMAA – β-N-methylamino-l-alanine. Bats in Guam, until they became extinct, ate a diet filled with the seeds of cycad trees, which contain BMAA. The BMAA contained in the cycad trees originates in what are called cyanobacteria that grow on the roots of the trees.
- The amino acid L-serine, which is available as a dietary supplement, may help protect against these types of brain problems and lower the risk of Alzheimer's disease. L-serine could possibly boost longevity. In research on the Ogimi inhabitants of Okinawa, some of the longest-living people on earth, a dietary analysis shows that they eat foods – like seaweed – that contain four times as much L-serine as the average American diet.
- Study: These Commonly Prescribed Drugs Are Linked to a Nearly 50% Higher Dementia Rate - Everything Zoomer - anticholinergic drugs (a class of drugs that includes some antidepressants, bladder antimuscarinics, antipsychotics and anti-epileptic drugs).
- etc??
- Treatment
- Ambroxol Hydrochloride Uses, Dosage, Side Effects - Drugs.com
- Parkinson’s-related dementia - Perhaps slowing down the progression of Parkinson’s. However, there was overall no difference in cognition between the placebo and treatment groups.
- This Cough Syrup Ingredient Might Actually Slow Dementia
- lecanemab and donanemab (discovered in 2013)
- very expensive - patients in the US pay between £20,000 and £25,000 for them - 2025
- apply to only a relatively small subset of the Alzheimer’s population
- treatment effect is small
- high costs of identifying suitable patients and monitoring them for side-effects with lumbar punctures and MRI scans
- One very serious potential side effect is brain swelling which has reportedly caused several deaths.
- The donanemab report shows that there is even a lack of clarity about whether the drugs work at all
- Researchers are now finding similarities between what happens in the brain in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
- Breakthrough Alzheimer’s drug slows down cognitive decline in dementia patients - The Brighter Side of News
- A decade-long study reveals that cholinesterase inhibitors may slow cognitive decline and reduce mortality in dementia with Lewy bodies. Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs) and memantine target symptoms but do not halt disease progression.
- Lewy body disease (LBD), which includes dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson’s disease with or without dementia, is an insidious neurodegenerative disorder. It’s second only to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in prevalence. ChEIs, including donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine, work by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter vital for memory and learning. Studies suggest these inhibitors offer some cognitive benefits.
- Wearable ultrasound? New tech targets trouble spots in the brain
- Eli Lilly says Alzheimer's drug donanemab slows early stage disease
- Ambroxol Hydrochloride Uses, Dosage, Side Effects - Drugs.com
- Cures? for Dementia
- Immune system discovery reveals potential solution to Alzheimer’s | EurekAlert!
- STING = stimulator of interferon genes = an immune molecule that drives the formation of the harmful plaques and protein tangles thought responsible for Alzheimer’s.
- STING deletion protects against amyloid ß–induced Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis - Thanos - 2025 - Alzheimer's & Dementia - Wiley Online Library
- New study suggests Alzheimer’s may be reversible
- One-dose nasal spray clears toxic Alzheimer's proteins to improve memory
- monoclonal antibody 2 (TTCM2) specifically detects and targets disease-relevant tau aggregates
- treatment alleviated short-term memory loss in mice with advanced tau aggregates
- Crucial to the therapy, was TTCM2’s engagement with TRIM21, an intracellular (inside the cell) antibody receptor, which facilitated the clearance of antibody-bound tau aggregates.
- “This method not only improves the delivery of therapeutic antibodies but also enhances their efficacy in clearing tau aggregates and improving cognitive functions.
- Nasal tau immunotherapy clears intracellular tau pathology and improves cognitive functions in aged tauopathy mice | Science Translational Medicine
- New Alzheimer’s Drug Dramatically Slows Disease Progression | Extremetech
- The Latest Alzheimer’s Drugs to Slow Down Progression of the Disease - And Top Ways to Prevent It - Everything Zoomer
- Two drugs have been shown this year to slow down progression of the disease when it is treated early. Both are ‘biologics’ - monoclonal antibodies (MABs) that clear amyloid from the brain.
With both lecanemab and donanemab, there is a reduction in the chance of moving to the next stage of the disease
- Expensive, with possible side effects
- Lecanemab (IV infusion) - Leqembi
- Donanemab (IV infusion) - Eli Lilly
- Aducanumab (Adulhelm) - Biogen
- New Alzheimer’s Drugs Offer Subtle Benefits - With Real Risks | WIRED
- Two drugs have been shown this year to slow down progression of the disease when it is treated early. Both are ‘biologics’ - monoclonal antibodies (MABs) that clear amyloid from the brain.
- ‘This looks like the real deal’: are we inching closer to a treatment for Alzheimer’s? | Health | The Guardian
- DNA "Scissors" Could Cut Out the Alzheimer's Causing Gene in Mice - CRISPR-Cas9
- FDA Grants Accelerated Approval for Alzheimer's Drug | FDA
- Aduhelm = aducanumab = a monoclonal antibody protein (targeting amyloid plaques) = introvenous treatment to slow (by ~20%) Alzheimer's = by Biogen (~$50,000/year)
- Very very controversial. Effectiveness depends on starting early enough and giving the patients a high enough dose for a long enough time. Side effects (like brain swelling and bleeding) are significant.
- Diet - Ketogenic ...
- A ketogenic drink improves cognition in mild cognitive impairment: Results of a 6-month RCT - Fortier - - Alzheimer's & Dementia - Wiley Online Library
- Quebec professor's drink to treat mild cognitive impairments in older adults hitting store shelves | CTV News - 30 grams of "medium-chain triglycerides" (MCTs from coconut oil and palm kernel oil) in the form of a liquid dietary supplement. MCTs enhance the body's production of ketones.
- Diet - Ketogenic ...
- A ketogenic drink improves cognition in mild cognitive impairment: Results of a 6-month RCT - Fortier - - Alzheimer's & Dementia - Wiley Online Library
- Alzheimer's disease: It may be possible to restore memory function, preclinical study finds - University at Buffalo
- Lithium?
- Fasudil?
- Role of Vitamin E in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from Animal Models
- The Role of Magnesium in Neurological Disorders
- David Perlmutter M.D. - Alzheimer's and Dementia - David Perlmutter M.D.
- L-serine
- Alzheimer’s breakthrough: British scientists pave way for simple pill to cure disease - Science - News - The Independent
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency Can Cause Symptoms That Mimic Aging - NYTimes.com -|$$$|- (CDN$20/4weeks)
- MayoClinic
- Neurobics.com
- Study: Older adults improve memory through exercise – The Chart - CNN.com Blogs
- Testing for dementia/Alzheimer - Predicting and Preventing Dementia
- See also: Vitamin D ...
- Scientists Identify a Trait in Speech That Foreshadows Cognitive Decline : ScienceAlert
- The pace of everyday speech may be a better indicator of cognitive decline than difficulty finding a word.
- The 'processing speed theory' argues that a general slowdown in cognitive processing lies at the very center of cognitive decline, not a slowdown in memory centers specifically.
- Speech patterns during memory recall relates to early tau burden across adulthood - Young - 2024 - Alzheimer's & Dementia - Wiley Online Library
- What is Alzheimer's disease? - YouTube
- BRIGHT MINDS—Proven Ways to Reduce the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia | Amen Clinics Amen Clinics
- Memory Rescue BRIGHT MINDS: Mental Health I Amen Clinics | Amen Clinics Amen Clinics
- Risk factors (memory & mental health): B = Blood Flow; R = Retirement/Aging; I = Inflammation; G = Genetics; H = Head Trauma; T = Toxins; M = Mental Health; I = Immunity/Infection Issues; N = Neurohormone Deficiencies; D = Diabesity; S = Sleep Issues
- Memory Rescue BRIGHT MINDS: Mental Health I Amen Clinics | Amen Clinics Amen Clinics
- FDA clears first blood test for Alzheimer’s detection | Honolulu Star-Advertiser
- Lumipulse = Fujirebio Diagnostics’ blood test to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease
- Lumipulse checks for two proteins in the blood and uses their ratio to help detect signs of amyloid beta plaque
- Partnering with therapy Leqembi by Biogen & Eisai
- C2N Diagnostics’ PrecivityAD2
- Partnering with therapy Kisunla by Eli Lilly
- Alternative tests
- Spinal tap, which requires an invasive puncture to collect spinal fluid
- PET brain scan ($$$) that may not be reimbursed by health insurers.
- Lumipulse = Fujirebio Diagnostics’ blood test to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease
- New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer's Up to 20 Years Before Symptoms Start - Everything Zoomer
- The blood test identifies biological markers in blood that show the build-up of the protein amyloid-beta — one of the first signs of Alzheimer's disease. Until now, reports Nature Magazine, the only way to identify amyloid-beta in the brain - short of an autopsy - has been to image the brain using PET scans, or to measure levels of the protein directly in cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal cord. Both of these procedures have been used to help recruit patients into recent trials, but the tests are expensive and uncomfortable.
- Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer's disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer's dementia | Nature Medicine - 2020-03-02
- Closer to a blood test for Alzheimer disease | Nature Reviews Neurology - 2020-03-18
- New Alzheimer's Blood Test Beats Cognitive Evaluations, Invasive Procedures | Extremetech
- New Blood Test Identifies Alzheimer’s With 97% Accuracy | Extremetech
- Predictors of dementia misclassification when using brief cognitive assessments | Neurology Clinical Practice - Neurology.org
- How Alzheimer's blood tests could speed up diagnosis, alter treatment
- Accumulations of molecules known as amyloid beta plaques and misfolded tau proteins (tangles) are believed to play a key role (see 101) but are challenging to detect and measure.
- The new test - called PrecivityAD2 - measures the ratios of both present in a patient’s blood, plugging the result into a proprietary algorithm to predict the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
- Alzheimer's Explained - YouTube
- Early dementia diagnosis: blood proteins reveal at-risk people
- DCTclock: Clinically-Interpretable and Automated Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Drawing Behavior for Capturing Cognition - PubMed
- Activity / Activities
- Durin Technologies Inc.
- Can Intermittent Fasting Stave Off Alzheimer’s Disease? - Everything Zoomer
- Scientists Develop Blood Test That Detects Alzheimer’s Years Before Onset - ExtremeTech - SOBA
- Memory Disorder Reduction and Prevention Practices - Thanks to Lindsay Allen for recommending this site.
- The 6 WARNING Signs of Dementia - YouTube
- Signs: Poor organization and planning, Personality changes, Constipation, Sensory dysfunction, Language problems, Problems navigating
- Prevention: Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) (nutritional yeast), Fix the gut (biome) (low carb diet & fasting), Consume broccoli sprouts, Ketones (fasting, MTC oil), Ginkgo Biloa (EGB 761), Lion's mane mushroom, (Omega-3, Vit.D, Zn=Zinc, Exercise, Sleep)
- Cognitive decline due to ageing can be reversed in mice – here's what the new study means for humans
- It has been known for some years that eating blueberries and other fruit and vegetables, such as strawberries and spinach, improves cognition in rodents and older people. These foods are rich in molecules such as resveratrol, fisetin and in quercetin, which have been shown either to kill or rescue senescent cells.
- Scientists could have a better way to spot early signs of dementia — Quartz
- Ultrasound neck scan to measure the intensity of "carotid artery forward compression waves." This is a measure of the force needed to propel blood to the brain. After taking age, blood pressure, body mass index, diabetes and other cardiovascular conditions into account, the researchers found those with the highest intensity pulses at the start of the study were 50 per cent more likely to suffer accelerated cognitive decline over the following decade. 51856, BHF, BBC-46155607
- Exercise ...
- Fitness
- Exercising, cutting stress, improving sleep, eating sensibly, and taking a few selected supplements (something as simple as enzymes can help).
- Midlife cardiovascular fitness and dementia | Neurology
- The Association Between Midlife Cardiorespiratory Fitness Levels and Later-Life Dementia
- Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications
- A meta-analytic review of the effects of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- How to cut your risk of memory loss - CNN.com
- Daily Consumption of Oregon Hazelnuts Affects a-Tocopherol Status in Healthy Older Adults: A Pre-Post Intervention Study | The Journal of Nutrition | Oxford Academic - (vitamin E, Magnesium)
- L-serine
- Klotho: Could This Protein Actually Be the Key to Longevity? - Everything Zoomer
- Sleep
- Dementia: The greatest health challenge of our time - BBC News
- Research estimates that one in three cases could be prevented by lifestyle changes including:
- treat hearing loss in mid-life
- spend longer in education
- don't smoke
- seek early treatment for depression
- be physically active
- avoid becoming socially isolated
- avoid high blood pressure
- don't become obese
- don't develop type 2 diabetes
- Research estimates that one in three cases could be prevented by lifestyle changes including:
- Many dementias could be prevented if nine lifestyle factors were corrected, resulting in about 30 per cent fewer people with dementia.
- low levels of education
- mid-life hearing loss
- physical inactivity
- high blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- obesity
- smoking
- depression
- social isolation.
- Care / Caring for Alzheimers
- Caring for Patients With Dementia and Alzheimer’s | Incredible Health - Thanks to Maggie Strife for recommending this site.
- Arts and Crafts for People with Alzheimer's | FindReviews - Thanks to Graham Cook for recommending this site.
- Alzheimer's Caregivers | MedlinePlus
- Alzheimer's and Dementia Home Safety Checklist - Thanks to Cory Sharp for recommending this site.
- ************
- see also: Dementia
- Resources for Memory/Alzheimer
- What Causes Alzheimer’s? Scientists Are Rethinking the Answer. | Quanta Magazine
- Alzheimer’s Breakthrough: Genetic Link to Gut Disorders Confirmed - Neuroscience News
- The Most Promising Research in the Race for a Dementia Cure - Everything Zoomer
- LATE
- Awakening From Alzheimers
- SAD = Standard American Diet (to be avoided)
- Regain Your Brain – Trailer - $0 online series
- ApoE4.Info – The Alzheimer's Gene Resource
- ApoE4.Info - Forums
- Dr. Dale Bredesen | The End of Alzheimer's | MPI Cognition
- APOE-4 allele. It is known that carrying this allele is associated with increased risk for Alzheimer's disease. APOE-4 allele (the APOE-4 allele is present in about 20-25% of the United States population). It is easy to test for this allele without involvement of a healthcare provider by simply trying a genetic testing product like 23 and Me.
- The Sleep Doctor - Michael J. Breus, PhD
- EndFatigue
- SHINE Protocol = Sleep + Hormones + Infection + Nutrition + Exercise (with sunshine)
- If a medical product/procedure is not profitable, it can't go through the FDA (USA) approval process. Inexpensive or natural/holistic products are not discussed in medical schools.
- Cures A-Z on the App Store
- Eating chocolate (one small square per day) is as much as 25 times more likely to prevent a heart attack than taking a Statin. (Unless you have a known heart disease.)
- Curamin (not to be confused with Curcumin) will reduce pain if taken 2-3 times a day for six weeks. More pain relief than Celebrex.
- Curcumin (included in CuraMed) will help with depression. More effective than anti-depressant drugs.
- Neurogenesis: How to Change Your Brain | HuffPost
- C-Health: Your Health and Wellness Source - powered by MediResource
- Canadian Health Network - Réseau canadien de la santé
- Canadian Living
- CNN
- CNN.com - Transcripts - Dr. Sanjay Gupta - A look at Alzheimer's Disease
- CNN.com - Transcripts - Dr. Sanjay Gupta - A Look at Treatments for Alzheimer's Disease
- Study: Older adults improve memory through exercise – The Chart - CNN.com Blogs - 2011-01-31
- How to cut your risk of memory loss - CNN.com
- Dummies
- EverythingZoomer
- Health Canada - Santé Canada
- HealthAfter50.com | UC Berkley School of Public Health | Health and Welness Alerts
- healthfinder® - your guide to reliable health information
- MayoClinic.com - Alzheimer's disease
- Montreal Gazette
- Dr. Rishanthi Sivakumaran creates reference points on the head of Micheline Morency at the Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation laboratory at the McGill research
- In Nigeria, Justice was once full of beans - By JOE SCHWARCZ, Freelance June 4, 2011
- http://www.montrealgazette.com/health/Nigeria+Justice+once+full+beans/4892260/story.html#ixzz1P78lIWd1
- Acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter needed to relay information from nerve to muscle cells
- The Calabar bean can serve as an antidote to atropine, the belladonna poison
- Since Alzheimer's disease is also characterized by an acetylcholine deficiency, physostigmine and its derivatives are also being explored in its treatment.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- National Library of Medicine - National Institutes of Health
- NLM Support Center - National Library of Medicine
- NY Times -|$$$|- (CDN$20/4weeks)
- Is Alzheimer’s Type 3 Diabetes?
- NYTimes.com - Signs of Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer’s Are Seen in Gait -|$$$|- (CDN$20/4weeks)
- Alzheimer's Disease - Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease - NY Times Health Information -|$$$|- (CDN$20/4weeks)
- How Exercise May Keep Alzheimer's at Bay - NYTimes.com -|$$$|- (CDN$20/4weeks)
- PLoS ONE : accelerating the publication of peer-reviewed science
- Prevention Magazine
- Smoking
- What Impact Does Smoking Have on Dementia Risk?
- WebMD
- Zoomer
- EverythingZoomer.com
- New Alzheimer's Drug Becomes First to Reportedly Slow Cognitive Decline in Trial - Everything Zoomer - donanemab
- Alzheimer's Awareness: Debunking 10 Common Myths - Everything Zoomer
- Omitted in this article: (see the Comments section at the bottom of the article)
- Alzheimer's may be a form of diabetes
- blood sugar levels, insulin levels
- dietary carbohydrates (low fat diets) vs. saturated fats (not trans-fats)(low carb diets)
- Omitted in this article: (see the Comments section at the bottom of the article)
- 10 Warning Signs of Alzheimer's - Everything Zoomer
- Memory loss that affects day-to-day function
- Difficulty performing familiar tasks
- Problems with language
- Disorientation of time and place
- Poor or decreased judgment
- Problems with abstract thinking
- Misplacing things
- Changes in mood and behaviour
- Changes in personality
- Loss of initiative