Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
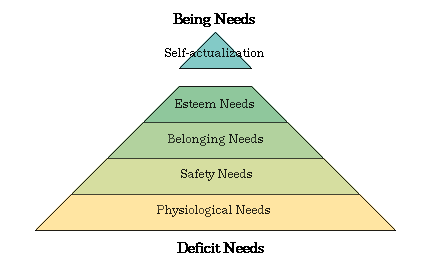
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- A model used as a framework for needs assessment.
- Motivation is based on satisfying a person's unmet needs
- needs that have been satisfied no longer provide motivation
- individual need categories can and do shift as circumstances change
- customers' needs, wants, demands
- needs = Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- wants = needs shaped by culture and individual personality
- demands = wants backed by buying power - people demand products and benefits that add up to the most value and satisfaction
- Motivation = the energizing force that causes behaviour that satisfies a need
- people have several different needs, which they attempt to satisfy in their work = people must fulfill lower-level needs before seeking to fulfill higher-level needs
- Levels of need = once one set of needs has been satisfied, it ceases to motivate behaviour = different people have different needs, so different things motivate different people
- once the lower needs are met, people seek to satisfy higher needs
- Levels of need (hierarchical)
- physiological = basic survival needs = oxygen, water, food, sex, sleep
- safety = security = freedom from harm, financial security = self-preservation and physical well-being = e.g. job security, pension plans
- social = friendship, companionship, belonging, love = feeling loved, accepted, part of the group = (a growth need) = affection
- personal needs = esteem = achievement, status, respect, prestige = recognition and acknowledgment from others, self-respect, sense of status = (a growth need) = e.g. job titles, large offices
- self-actualization = self-fulfillment = developing your full potential = achievement = (a growth need)
= e.g. grow and develop one's capabilities, achieve new and meaningful goals, challenging job assignments
- self-actualized persons are achievers
- Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs - Human needs are arranged in a hierarchy. A person tries to satisfy the most important need first. As each important need is satisfied, the next most important need will come into play."
- Physiological needs ► Safety needs ► Social needs ► Esteem needs ► Self-actualization needs
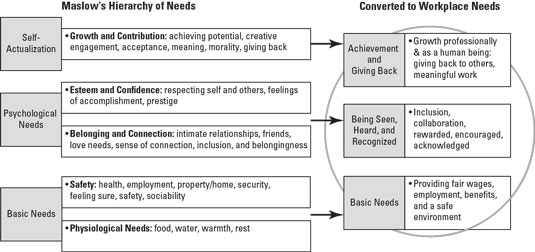 Trust and Needs in the Workplace
Trust and Needs in the Workplace- See also: Motivation ...

 Trust and Needs in the Workplace
Trust and Needs in the Workplace